The cut sinus signal is the output of a Dimmer or a thyristor driven AC controller. That’s one of the most frequent harmonics creators in the mains.

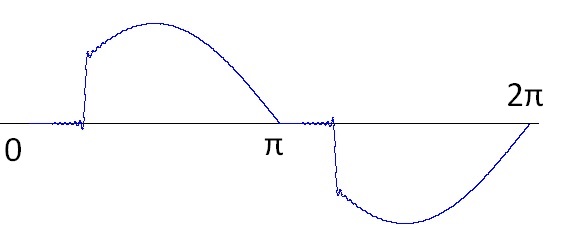
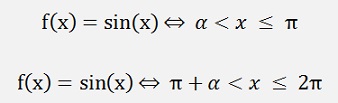
For the ak elements:
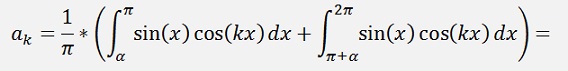
as
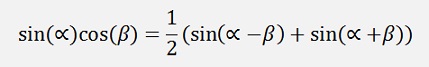
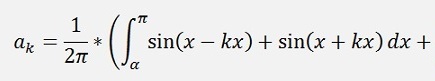
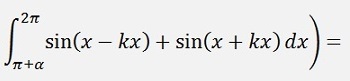
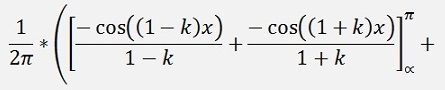
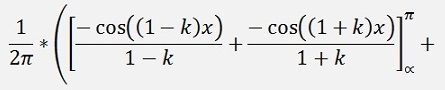
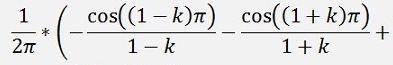
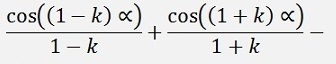

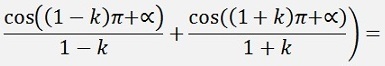
If k > 1
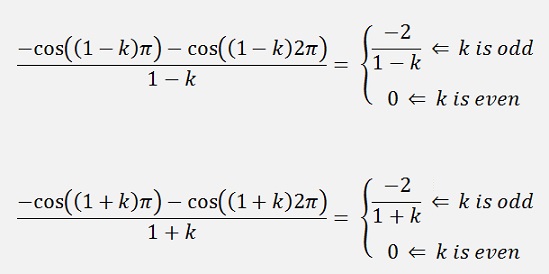
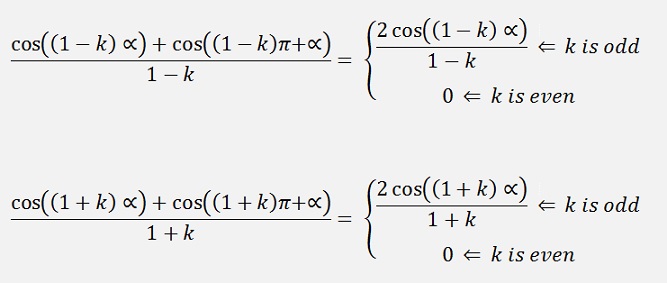
And therefore
If k is odd
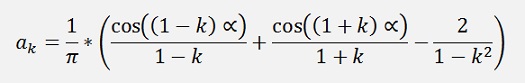
K is even
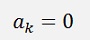
If k= 1
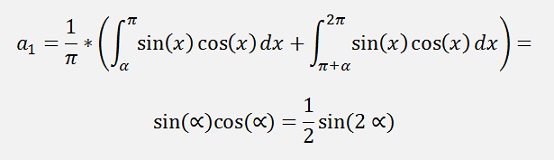
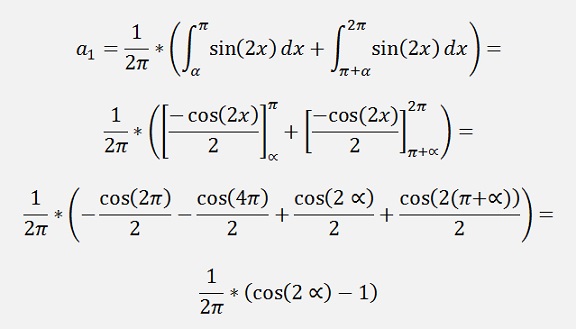
For the bk elements:
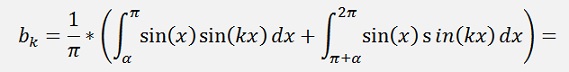
as
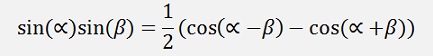
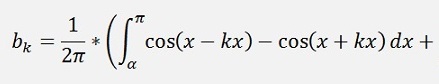
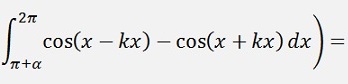
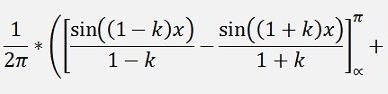
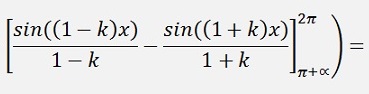
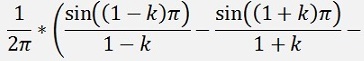
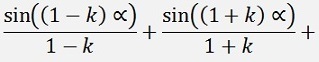
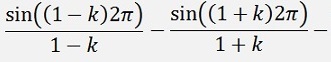
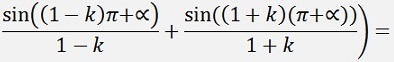
with
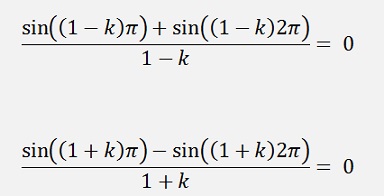
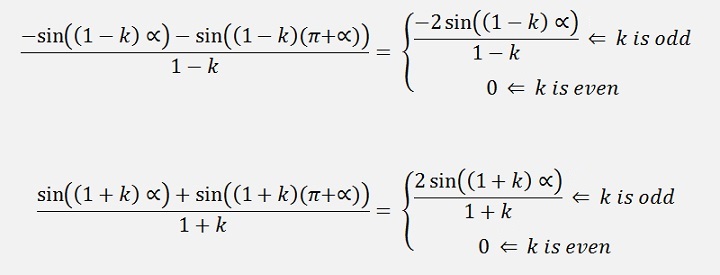
If k is odd
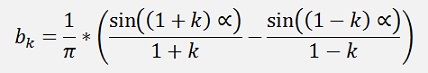
If k is even
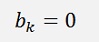
If k = 1
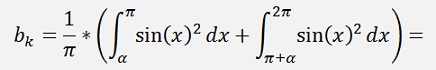
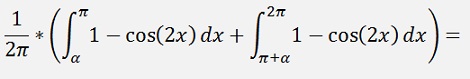
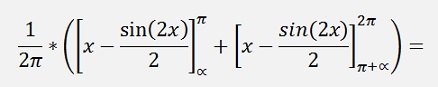
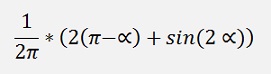
Put into code that’s;
private void SinusCut(double peak, double alpha)
{
int
j;
fft.c[0].real = 0;
for (j = 1; j < 500; j++)
{
}fft.c[0].real = 0;
for (j = 1; j < 500; j++)
{
if
(j % 2 == 0)
{
else
{
}{
fft.c[j].real
= 0;
fft.c[j].imag = 0;
}fft.c[j].imag = 0;
else
{
if
(j == 1)
{
}
else
{
}{
fft.c[j].real
= peak / Math.PI
/ 2.0 * (Math.Cos(2.0
*
alpha) - 1.0);
fft.c[j].imag = peak / Math.PI / 2.0 * (2.0 * (Math.PI - alpha) + Math.Sin(2.0 * alpha));
fft.c[j].imag = peak / Math.PI / 2.0 * (2.0 * (Math.PI - alpha) + Math.Sin(2.0 * alpha));
}
else
{
fft.c[j].real
= peak / Math.PI
* (Math.Cos(alpha
* (1.0 -
j)) / (1.0 - j) + Math.Cos(alpha
* (1.0 +
j)) / (1.0 + j) - 2.0 / (1.0 - j * j));
fft.c[j].imag = peak / Math.PI * (Math.Sin(alpha * (1.0 + j)) / (1.0 + j) - Math.Sin(alpha * (1.0 - j)) / (1.0 - j));
}fft.c[j].imag = peak / Math.PI * (Math.Sin(alpha * (1.0 + j)) / (1.0 + j) - Math.Sin(alpha * (1.0 - j)) / (1.0 - j));
And the spectrum for α = 40° and the first 30 harmonics:
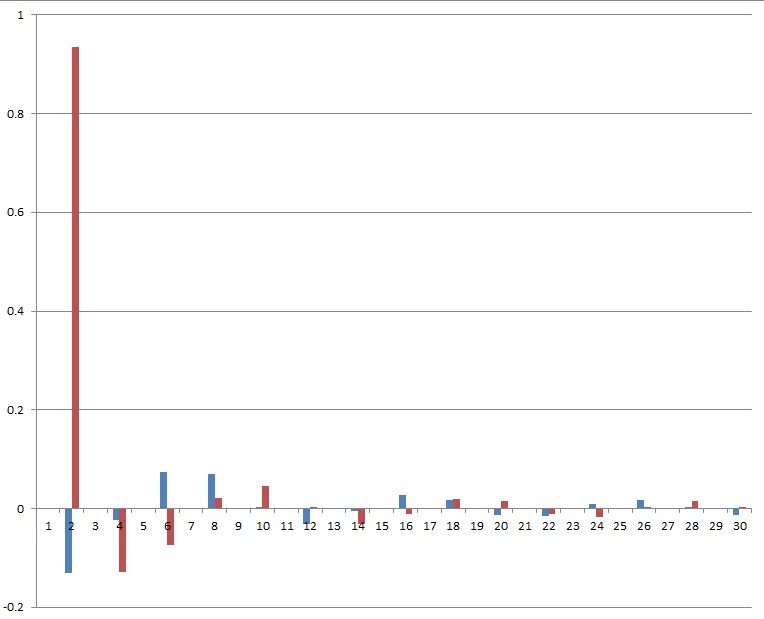
Blue are the real elements and red the imaginary parts.
And if all the harmonics are put together, we get the signal shape. The brightest line is the base frequency. The next darker is the base frequency plus the first harmonic, then comes the same plus the next harmonic … and so on. The more harmonics are included, the closer the shape approximates the origin shape.
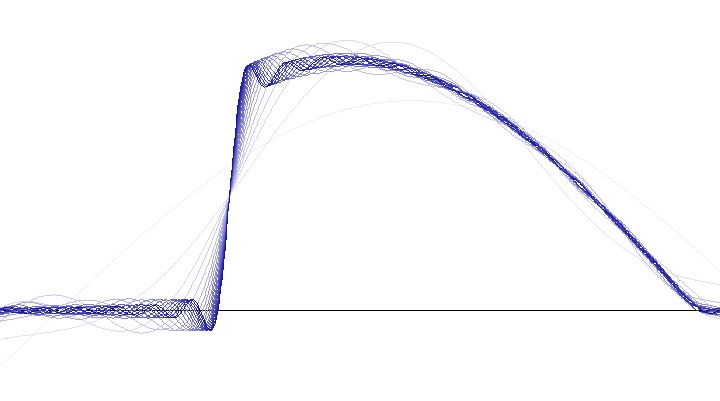
C# Demo Project Fourier signals

